3.1 - Diagnosis
Road Test
Always confirm the complaint by testing the vehicle on the road first. This will help direct the diagnosis and reduce diagnostic time.
Visual Inspection
Perform a complete visual inspection of the fuel delivery system's components. Before condemning the fuel pump, properly inspect and test the fuel delivery system according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Underhood lines/hoses
- Undercar lines
- Fuel tank
- Fuel filter
- Fuel filler neck
Test the fuel pressure. If the fuel pressure is incorrect, even as little as two pounds, this will affect engine performance. Proper system analysis must be performed to locate the fault.
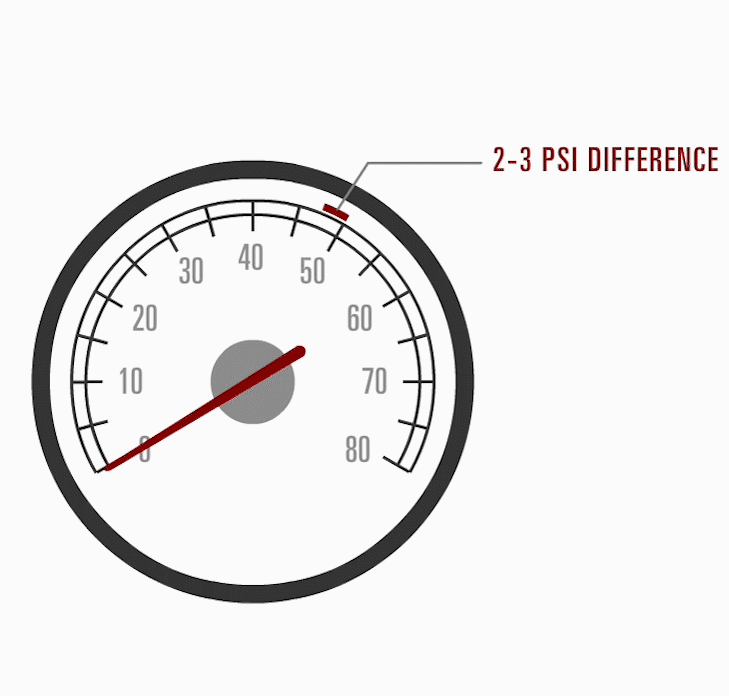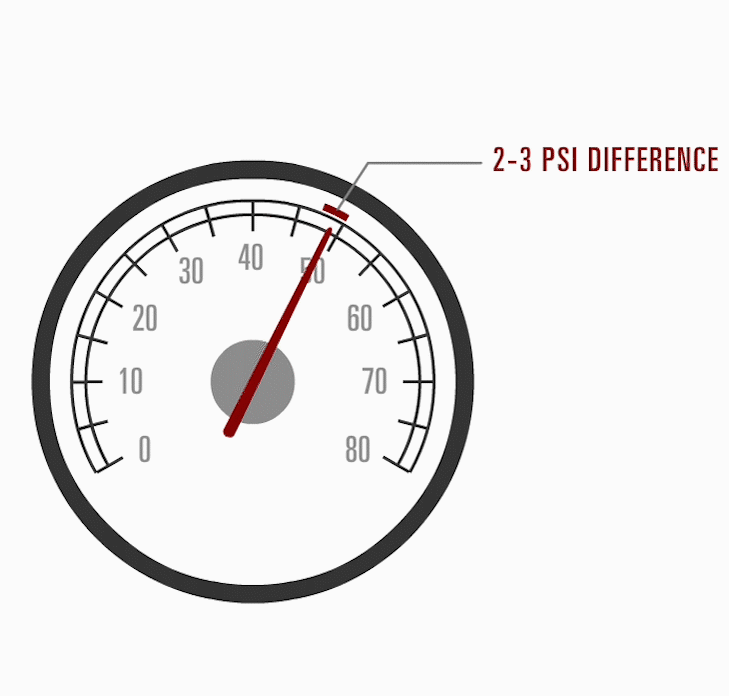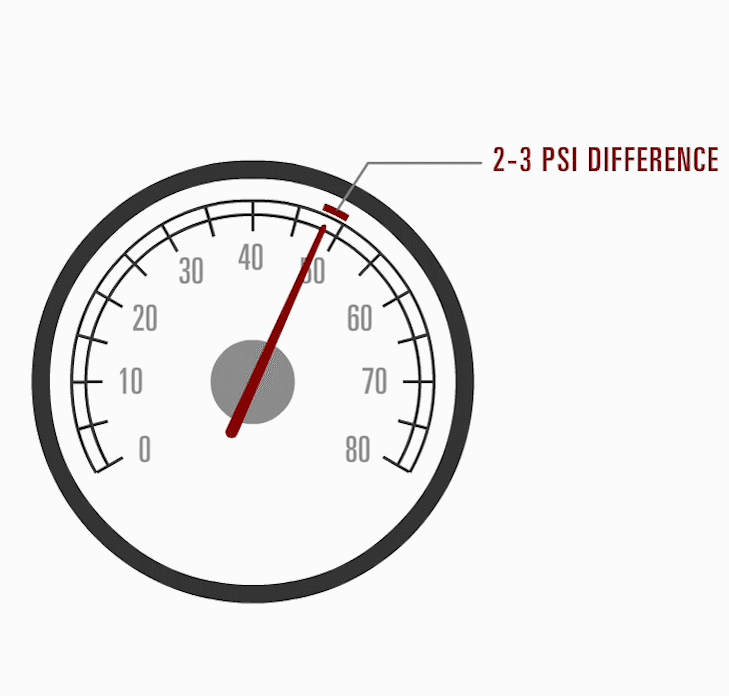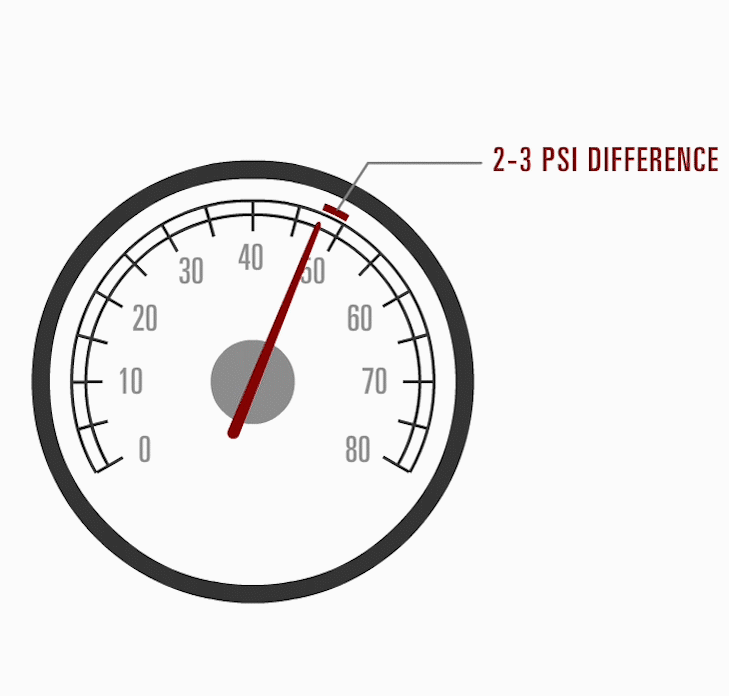
Fuel Pressure Testing
To diagnose fuel pressure-related problems, a fuel pressure gauge must be installed on the pressure line.
Many models have a service port to access the fuel pressure. Others must be opened for the installation of appropriate adapters when necessary.
Ensure that the system can hold pressure: if not, the possible causes are the regulator not seating properly, a defective pump check valve, or a possible system leak.
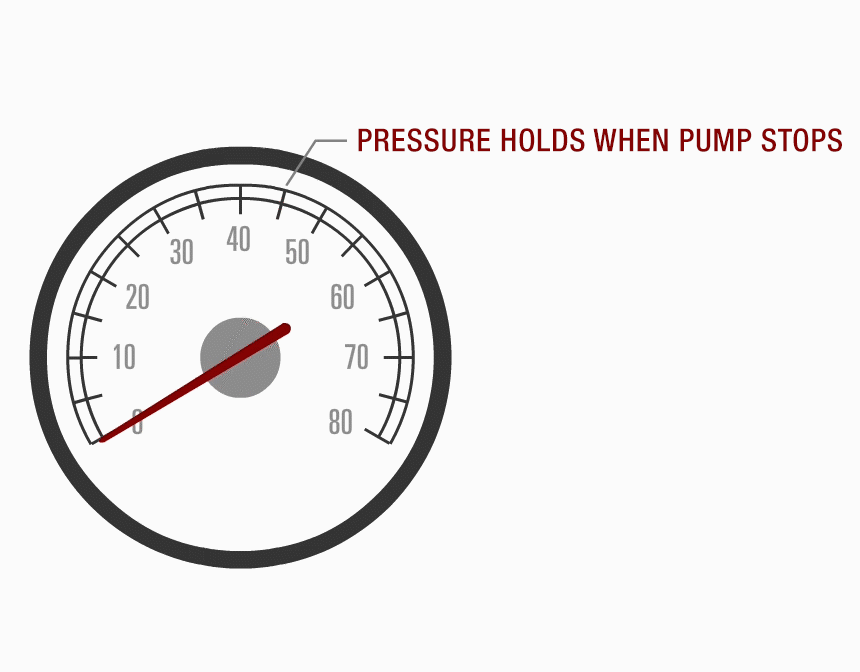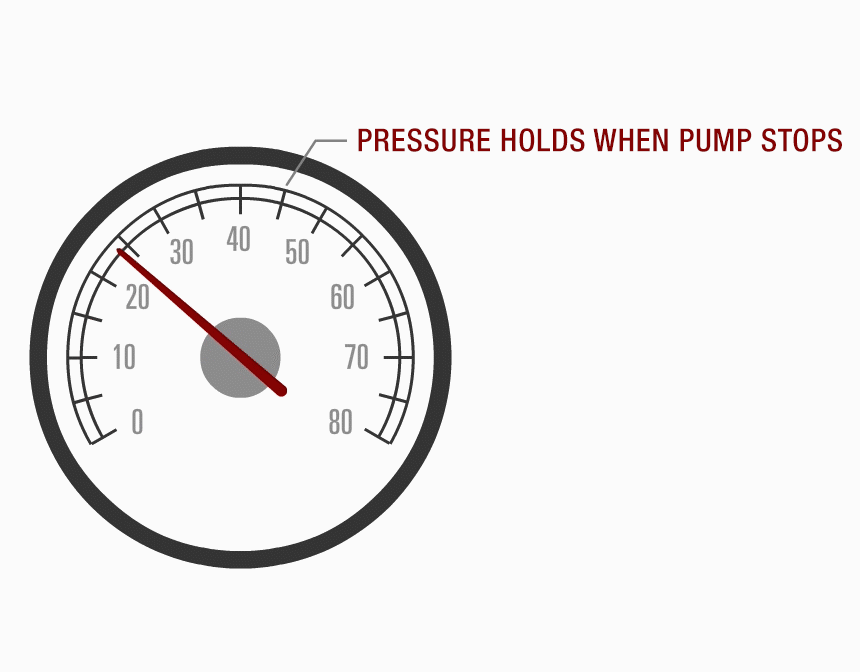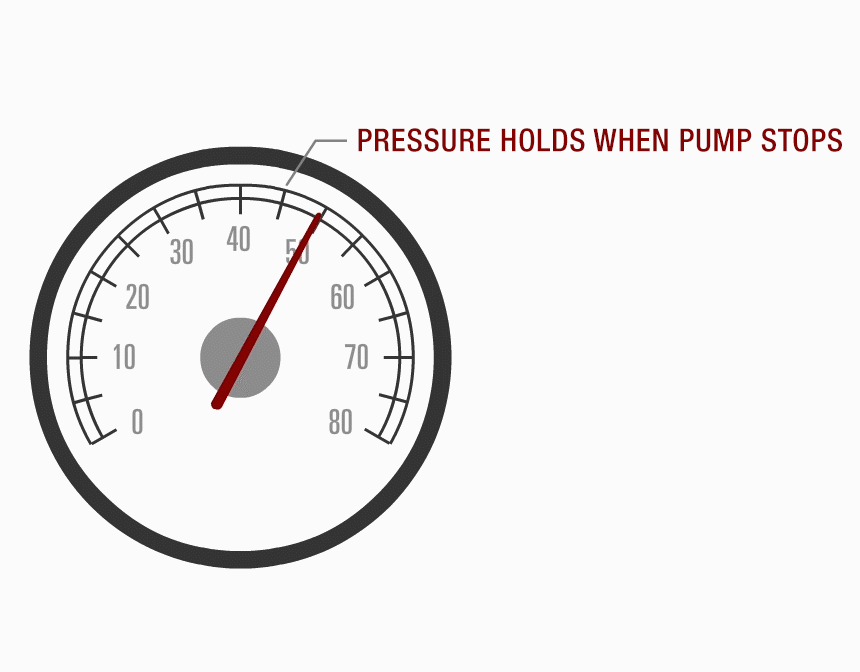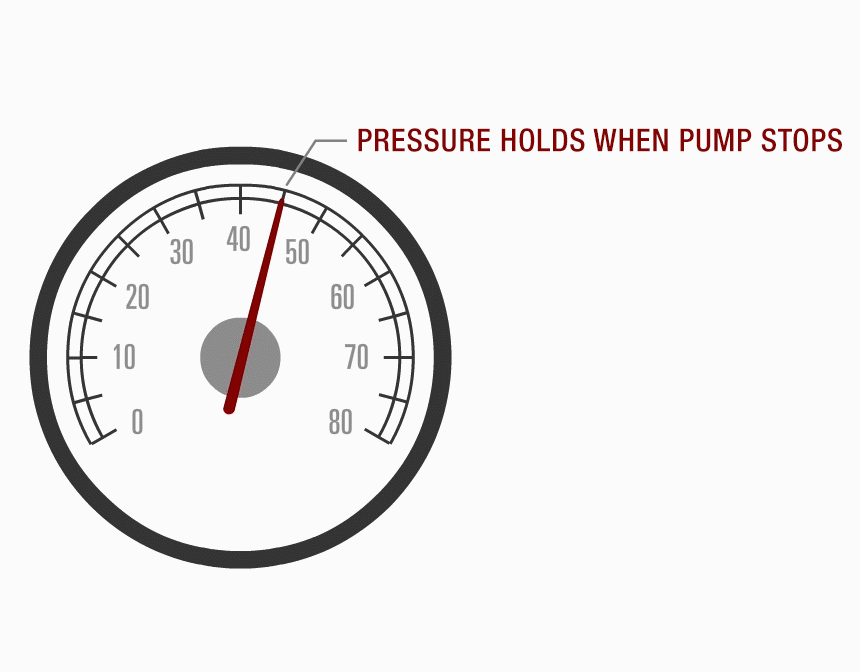
Performance Scan Test
Perform a scan test. Most electronic fuel injection systems do not monitor the fuel delivery system.
All fuel delivery problems are determined by trouble codes related to performance rather than actual pump and fuel circuit.
Newer models are now equipped with fuel pressure and temperature sensors to monitor the delivery system.